CocoIndex Changelog 0.3.11 - 0.3.26
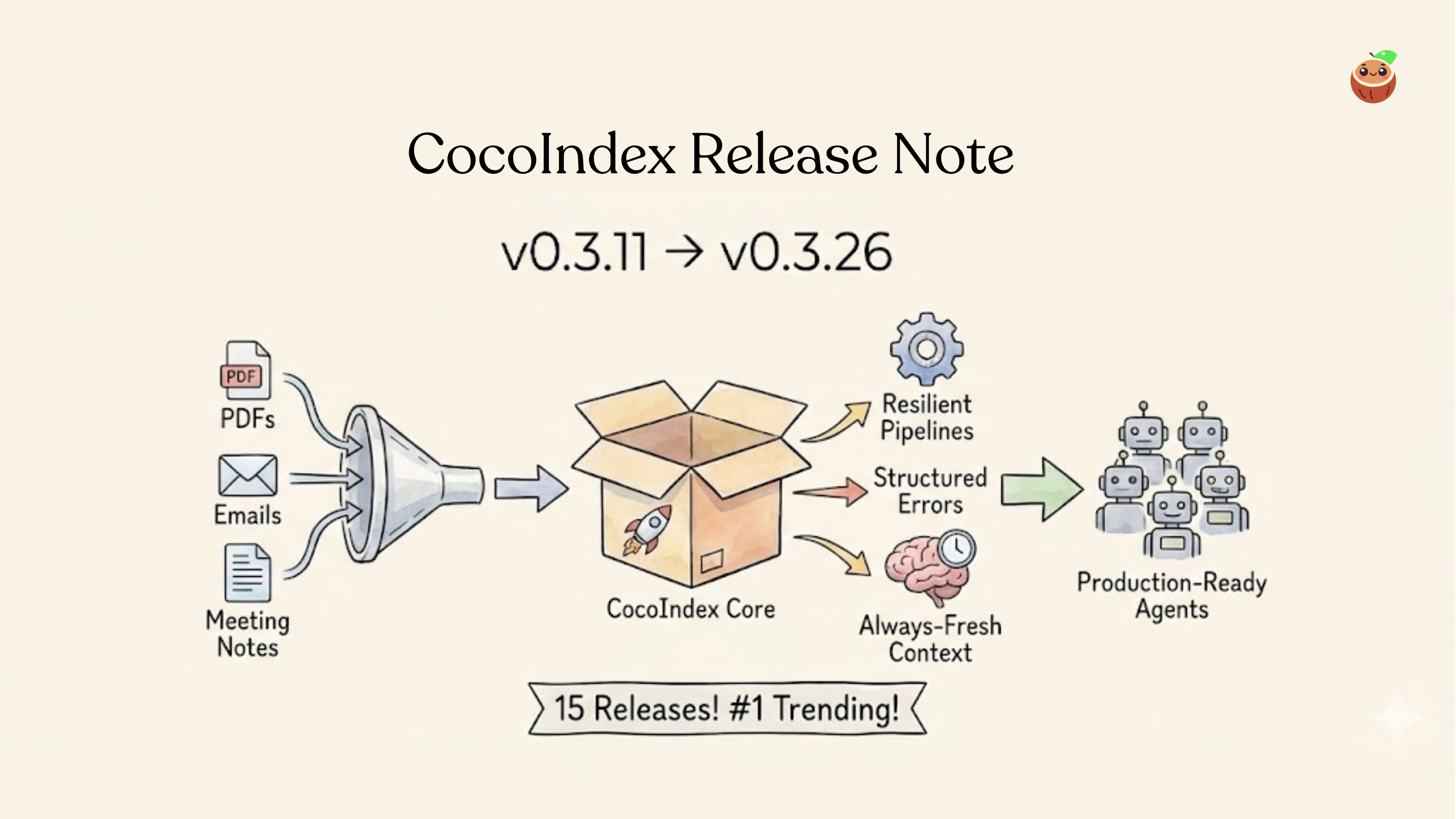
CocoIndex is moving at insane speed! 🚀 Since the last release, CocoIndex shipped 15 releases (0.3.11–0.3.26) and crossed a major milestone—# GitHub Global Trending across all languages and #1 on Rust. This cycle was focused on one clear goal: making fresh, structured, programmable context reliable enough for agents running in production.
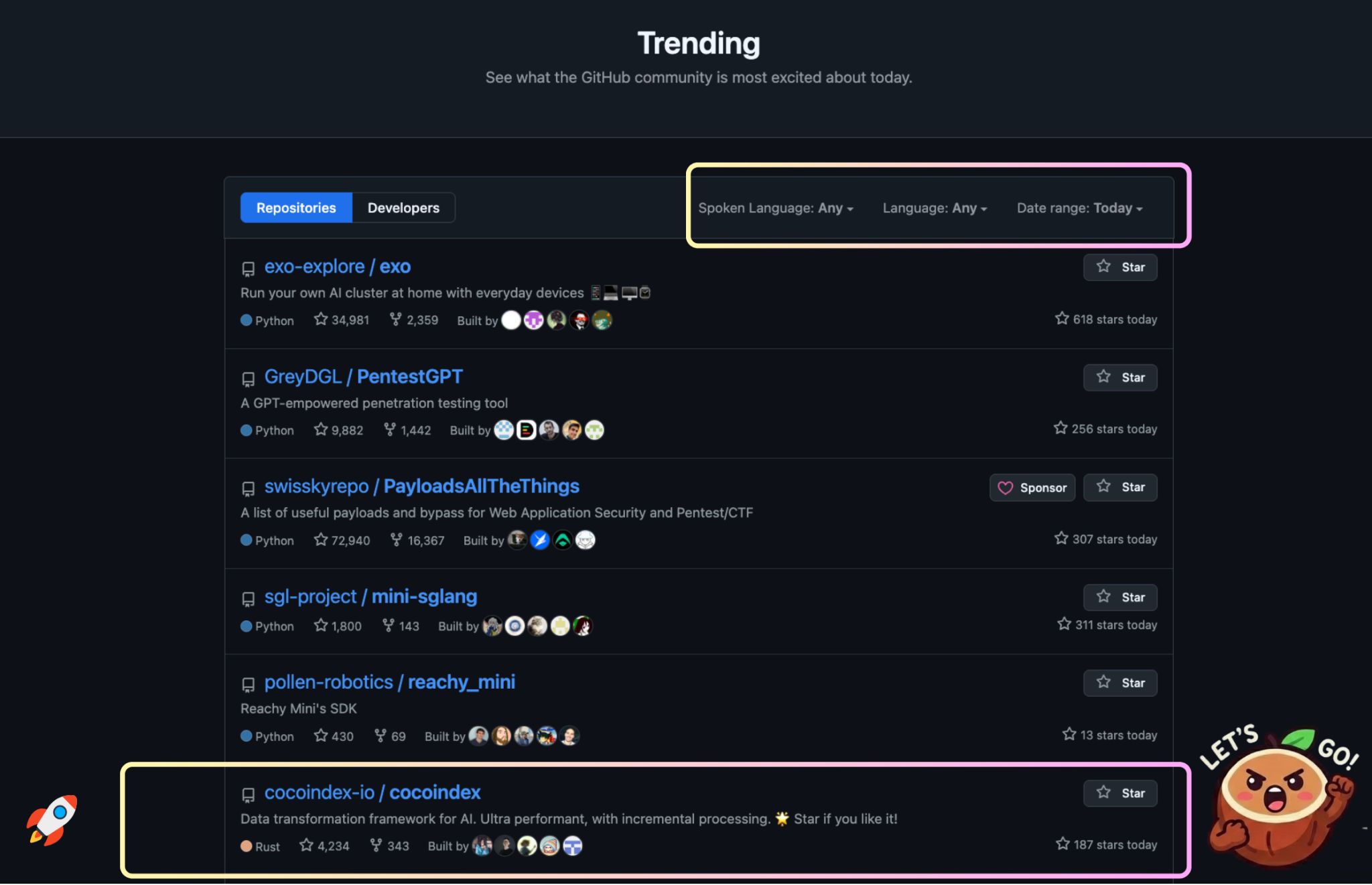
Agents are only as good as the data they reason over. Thinking about codebase, meeting notes, emails, relationships, commerce ... anything that may subject to change. If you ever done index-swap or have to keep multiple copies of target to serve live agents on data or code change, you'll never have to do it again.
CocoIndex helps you ace the data for agents without heavy data engineering work. — Continuous fresh, structured and programmable context for AI, from PDFs, Codebase, Emails, Screenshots, Meeting Notes, ... — always up-to-date, at any scale, ultra-performant, with a smart incremental engine. ⭐ Star the repo
Glad this project resonates with the community! 2026 will be more autonomous agents going production and excited to see CocoIndex help in that frontier.
Here what we shipped since last release - 0.3.11–0.3.26 was about production trust: resilient pipelines, structured errors, better observability, and always-fresh structured context for agents operating in the real world.
Core capability
CocoIndex just got a significant upgrade in runtime resilience and developer ergonomics. The core engine now also features a fully structured error system, enabling unified error tracing from Rust to Python so you can finally see human‑readable stack traces across boundaries. Combined with smarter runtime warnings for slow live updates, simplified progress bar rendering, and cleaner internal API boundaries, CocoIndex continues to evolve into the most transparent and trustworthy data‑processing core in its class.
Failure-tolerant target deletion
Target drop failures no longer block pipeline setup updates — an environment toggle COCOINDEX_IGNORE_TARGET_DROP_FAILURES lets you log and continue gracefully (#1454).
Simplified progress experience
Streamlined progress bar updates for a more predictable runtime visualization experience (#1467).
Structured error system overhaul
A new foundation for error definition and propagation:
- Introduced structured error framework with host exception tunneling
- End-to-end Python stack trace propagation now supported
- New unified error types improve exception messaging and logging at both Rust and Python layers (#1380, #1413).
Smart runtime alerts
CocoIndex now warns when live updates exceed the configured refresh interval—ideal for maintaining freshness guarantees (#1408).
Cleaner internal API boundaries
Refactored datatype.py with a dedicated _internal module, decluttering the public API surface (#1402).
Force reprocessing option for updates
Added explicit control for full recomputation during incremental updates for safer state resets. Run cocoindex update --full-reprocess ... flag to force a reprocessing (#1385).
Flow correctness improvements
- Fixed target diffing logic for user-managed setup states
- General FTS fixes for LanceDB (#1369, #1403)
Together, these changes strengthen the core runtime's fault tolerance, improve observability, and lay the groundwork for a richer developer debugging experience.
Integrations
This release massively expands what CocoIndex can plug into.
Sources & targets
Qdrant
Full support for VectorIndexMethod HNSW configuration (#1410).
Postgres
Native support for pgvector types in Postgres source (#1387).
Local files
Automatic symlink resolution for easier graph ingestion (#1463).
LanceDB
- Added
optimize()for post-ingest table compaction - Extended full-text search integration (#1466, #1358)
Functions & LLM providers
Unified OpenAI/Azure architecture
Shared logic between openai.rs and azureopenai.rs for cleaner code reuse (#1376).
Azure OpenAI integration
Bring your Azure LLM accounts seamlessly into CocoIndex pipelines (#1362).
OpenRouter embeddings
Added embedding model support across OpenRouter's expanding provider network (#1359).
Embedding dimension validation
Introduced expected_output_dimension param to enforce vector consistency (#1373).
Direct JSON output in functions
GeneratedOutput enum now supports structured JSON returns for downstream consumption (#1395).
Gemini API key fixes
Cleaner, more consistent propagation of credentials across function calls (#1375).
These integrations make CocoIndex a more open, extensible, and multi-LLM-ready data processing cortex.
Build with CocoIndex
We are having more projects build with CocoIndex.
Build fresh data with LanceDB and CocoIndex
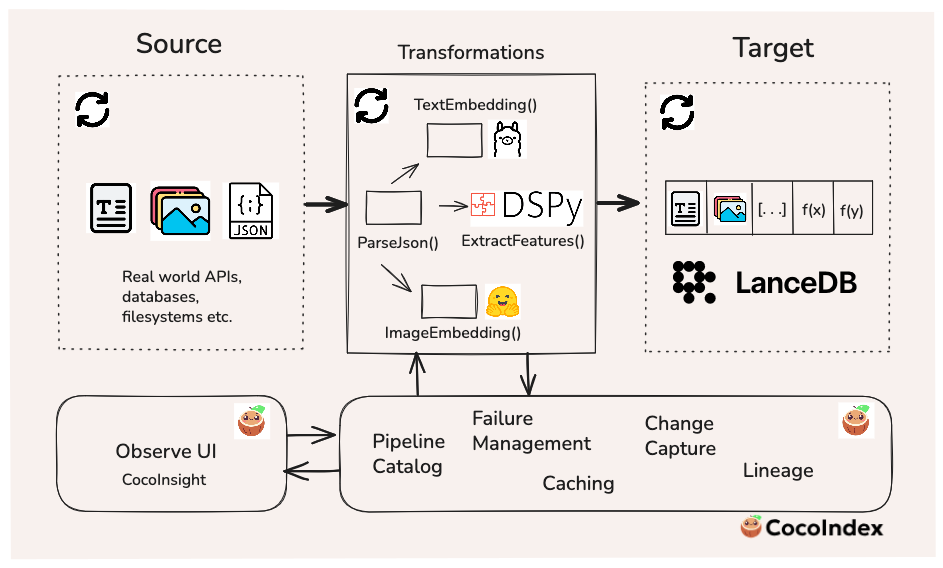
🚀 If agents are going to search, reason, and act over long periods of time, we need infrastructure that treats data freshness and multimodal as a first-class primitive.
Our friends at LanceDB just published a full walkthrough with us showing how to build a live-updating multimodal search index using LanceDB and CocoIndex, where text, images, embeddings, and LLM-derived features stay continuously in sync as data and logic evolve.
Checkout the tutorial for more details.
🔥 What's cool about this example:
- Incremental-by-design processing — Only new or changed records are reprocessed. Add one recipe? Update one image? Fix one ingredient? CocoIndex touches only what changed — not the other 100k rows.
- True multimodal indexing — Text, images, embeddings, and metadata live together in LanceDB — optimized for both search and analytics, without splitting data across systems.
- Schema evolution without rewrites — We add new LLM-extracted feature columns (vegetarian, dairy, category, etc.) after data is already live. CocoIndex updates the schema and backfills safely — no table rebuilds.
- Structured LLM extraction (no brittle prompts) — DSPY signatures define input/output types, so LLMs behave like programs — not JSON-generating slot machines.
- Upserts + deletes handled automatically — Primary keys + incremental flows mean no duplicates, no stale rows, no "did this record change?" logic to maintain.
- End-to-end lineage & observability — With CocoInsight, you can see exactly why a record changed and which transformation produced each field.
- Live mode for agent-ready systems — Run the pipeline continuously. As data arrives or logic changes, your search layer updates in near real time.
Think PDFs, slides, screenshots, images, videos, and support tickets across massive enterprise data lakes—all kept fresh, indexed, searchable, and generating real insights.
Building a real-time HackerNews trending topics detector with CocoIndex
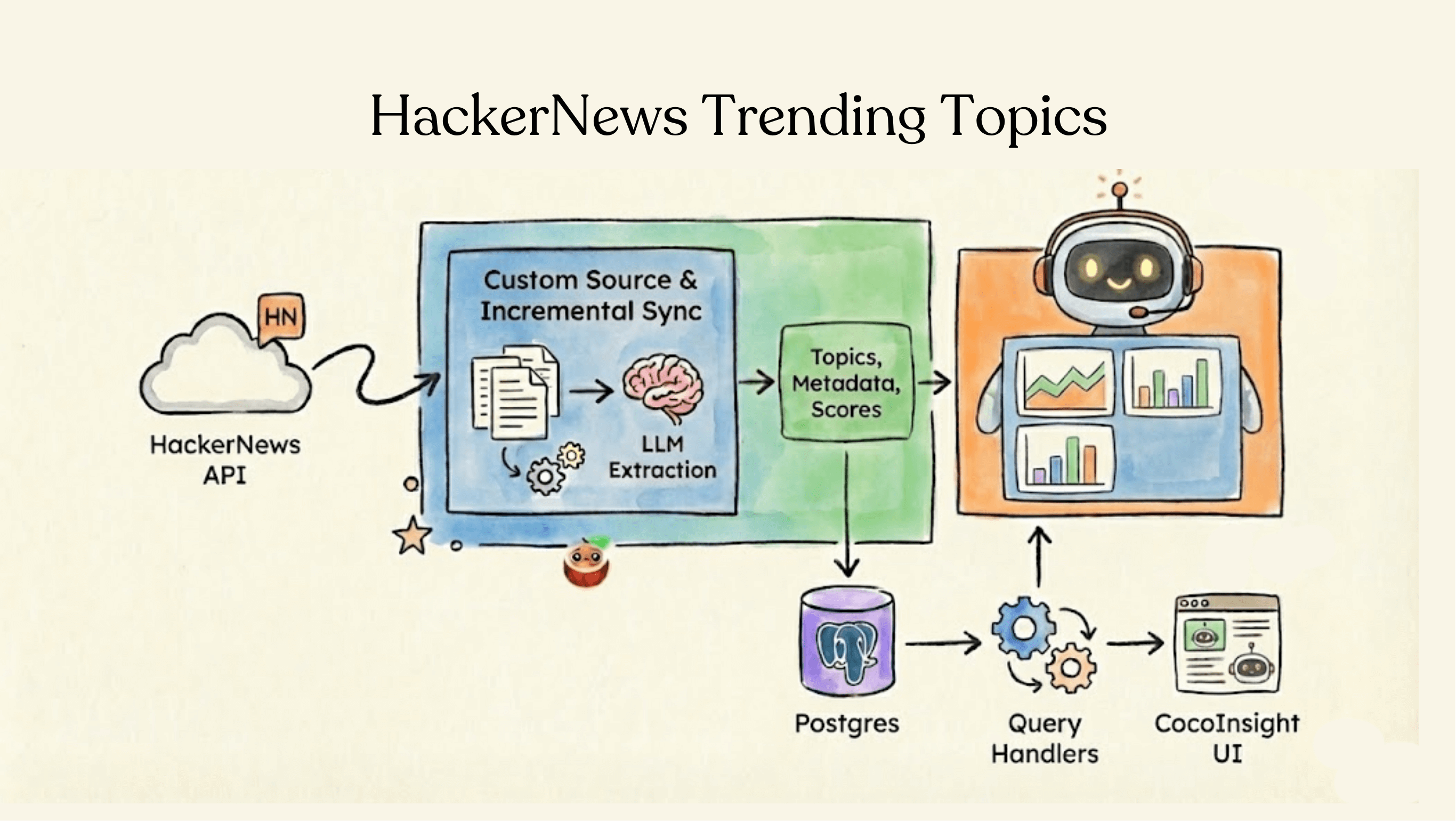
In the age of information overload, understanding what's trending—and why—is crucial for developers, researchers, and data engineers. HackerNews is one of the most influential tech communities, but manually tracking emerging topics across thousands of threads and comments is practically impossible.
In this post, we'll explore how to build a production-ready, real-time trending topics pipeline on top of HackerNews using CocoIndex. It shows how unstructured, high-volume community data can be incrementally ingested, enriched with LLMs, and queried as structured, up-to-date knowledge.
Each HackerNews thread and comment is then processed through an LLM-powered extraction step to identify normalized topics (technologies, products, companies, people, etc.). These topics, along with the original messages, are indexed into Postgres as queryable tables. Weighted scoring distinguishes primary topics in threads from secondary mentions in comments, enabling higher-quality trend rankings.
The result is a continuously updating system that turns raw HackerNews activity into structured, queryable intelligence—ready for dashboards, analytics, or AI agents.
Checkout the blog for more details.
Building a knowledge graph from meeting notes that automatically updates
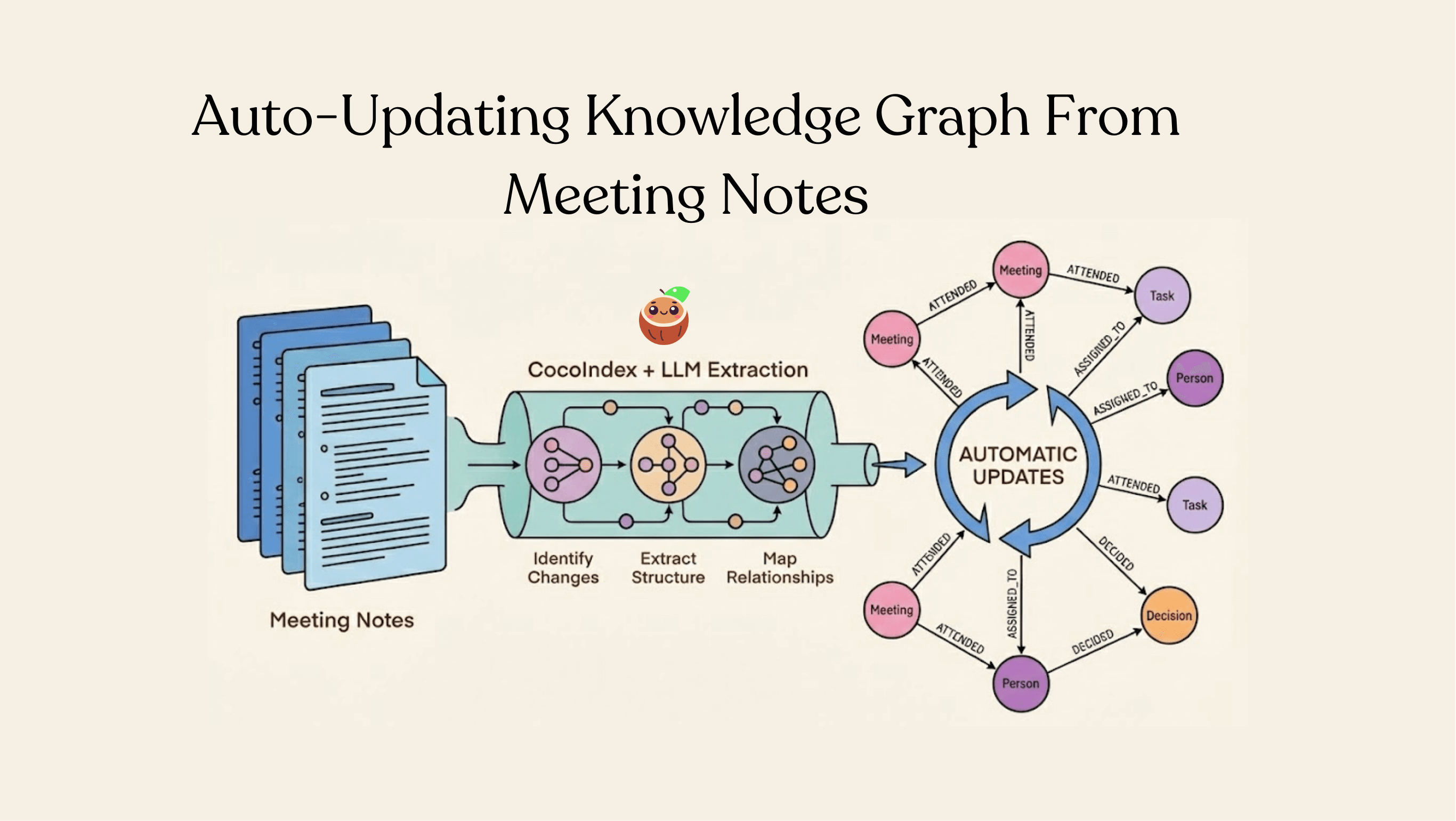
Most companies sit on an ocean of meeting notes, and treat them like static text files. But inside those documents are decisions, tasks, owners, and relationships — basically an untapped knowledge graph that is constantly changing. We just published a full walkthrough showing how to turn meeting notes in Drive into a live-updating knowledge graph using CocoIndex + LLM extraction.
Checkout the tutorial for more details.
What's cool about this example:
- Incremental processing — Only changed documents get reprocessed. If you have thousands of meeting notes, but only 1% change each day, CocoIndex only touches that 1% — saving 99% of LLM cost and compute.
- Structured extraction with LLMs — We use a typed Python dataclass as the schema, so the LLM returns real structured objects — not brittle JSON prompts.
- Graph-native export — CocoIndex maps nodes (Meeting, Person, Task) and relationships (ATTENDED, DECIDED, ASSIGNED_TO) without writing Cypher, directly into Neo4j.
- Real-time updates — If a meeting note changes — task reassigned, typo fixed, new discussion added — the graph updates automatically.
Extracting structured data from patient intake forms with DSPy and CocoIndex
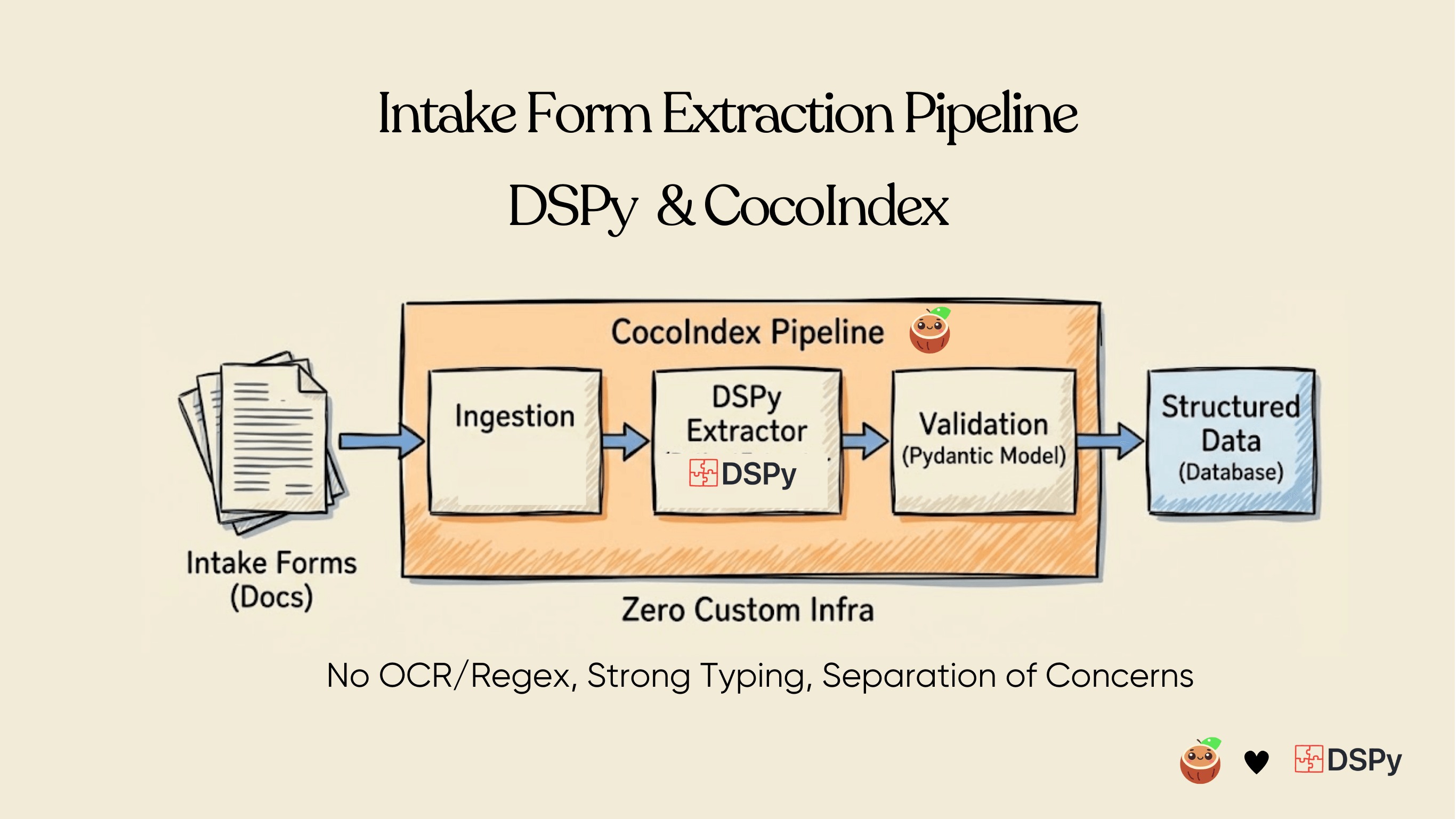
Patient intake forms are indeed a rich source of structured clinical data, but traditional OCR + regex pipelines fail to reliably capture their nested, conditional, and variable structure, leaving most of that value locked in unstructured text or manual entry.
This project demonstrates a production-ready approach to extracting clean, validated, structured patient data directly from PDF intake forms using DSPy and CocoIndex—without brittle OCR pipelines, regex rules, or Markdown intermediates.
The result is a scalable, explainable, and compliant pipeline well-suited for healthcare and other regulated domains—turning unstructured intake forms into always-fresh, queryable patient models ready for downstream systems, analytics, or AI agents.
Checkout the tutorial for more details.
Thanks to the community 🤗🎉
Welcome new contributors to the CocoIndex community! We are so excited to have you!
@1fanwang
@vipulaSD
@prrao87
@Haleshot
Thanks @Haleshot for improving the README note for better GitHub rendering in #1288, shifting to the tracing crate for logging in #1363, adding Postgres server reminder to quickstart docs in #1368, fixing the broken workflow badge in README in #1370, introducing a structured error system with host exception tunneling in #1380, adding llms.txt file to docs in #1455, adding short flag aliases for common CLI options in #1458, and adding env file sourcing tip to meeting_notes_graph example in #1470.
@thisisharsh7
Thanks @thisisharsh7 for making openai.rs generic to share logic with azureopenai.rs in #1376, including mypy type checking for the examples directory in #1383, and adding the GeneratedOutput enum for direct JSON returns in #1395, enhancing type safety and code reusability.
@prithvi-moonshot
Thanks @prithvi-moonshot for adding onBrokenAnchors config to report documentation errors in #1325, providing an option to force reprocessing during update in #1385, and making target deletion (drop) tolerate failures in #1454, improving robustness of the data pipeline.
@skprasadu
Thanks @skprasadu for wrapping cargo test to avoid embedded Python stdlib discovery crash in #1398, moving Query Support above Built-in Sources in the docs for better organization in #1397, and adding a warning when live update pass exceeds refresh_interval in #1408.
@Gohlub
@wxh06
@samojavo
@aryasoni98
Thanks @aryasoni98 for enabling programmatic API key passing besides reading from environment variables in #1134, providing more flexibility in configuration.
@shinobiwanshin
Thanks @shinobiwanshin for enhancing the Button component with hover effects and styling improvements in #1393, making the UI more polished and interactive.
@majiayu000
Thanks @majiayu000 for adding VectorIndexMethod support for HNSW configuration in Qdrant in #1410, enabling more fine-grained control over vector indexing parameters.
Summary
CocoIndex continues evolving into a resilient, intelligent data engine for the modern AI stack.
This cycle focuses on error transparency, LLM integration depth, and frictionless developer operations—ensuring your pipelines stay alive, observable, and blazing fast even under adverse conditions.
If you like this project, please support us with a star ⭐ at https://github.com/cocoindex-io/cocoindex !
🔥🔥 We are cooking something big! - v1 coming soon and stay tuned! If you read all the way here, you are a true fan!