Bring your own data: Index any data with Custom Sources

We’re excited to announce Custom Sources — a new capability in CocoIndex that lets you read data from any system you want. Whether it’s APIs, databases, file systems, cloud storage, or other external services, CocoIndex can now ingest data incrementally, track changes efficiently, and integrate seamlessly into your flows.
After this change, users for CocoIndex are not bounded by any connectors, targets or some prebuilt libraries. You can use CocoIndex for anything, and enjoy the robust incremental computing to build fresh knowledge for AI.
Custom sources are the perfect complement to custom targets, giving you full control over both ends of your data pipelines.
🚀 Get started with custom sources by following the documentation now.
Why not build another thousands of connectors?
Well, we could, and in fact, expanding our connector library is on the roadmap. However, enterprise software doesn’t just need more connectors. The challenge isn’t simply plugging into APIs — data is often siloed behind complex systems, inconsistent schemas, and fragile integrations. Building connectors alone doesn’t solve the underlying problems of reliability, observability, and incremental updates. What enterprises truly need is a robust infrastructure that can handle ever-changing datasets, reconcile differences across systems, and ensure data flows are durable, efficient, and error-resilient. That’s where we focus: not just connecting, but orchestrating data with intelligence and resilience.
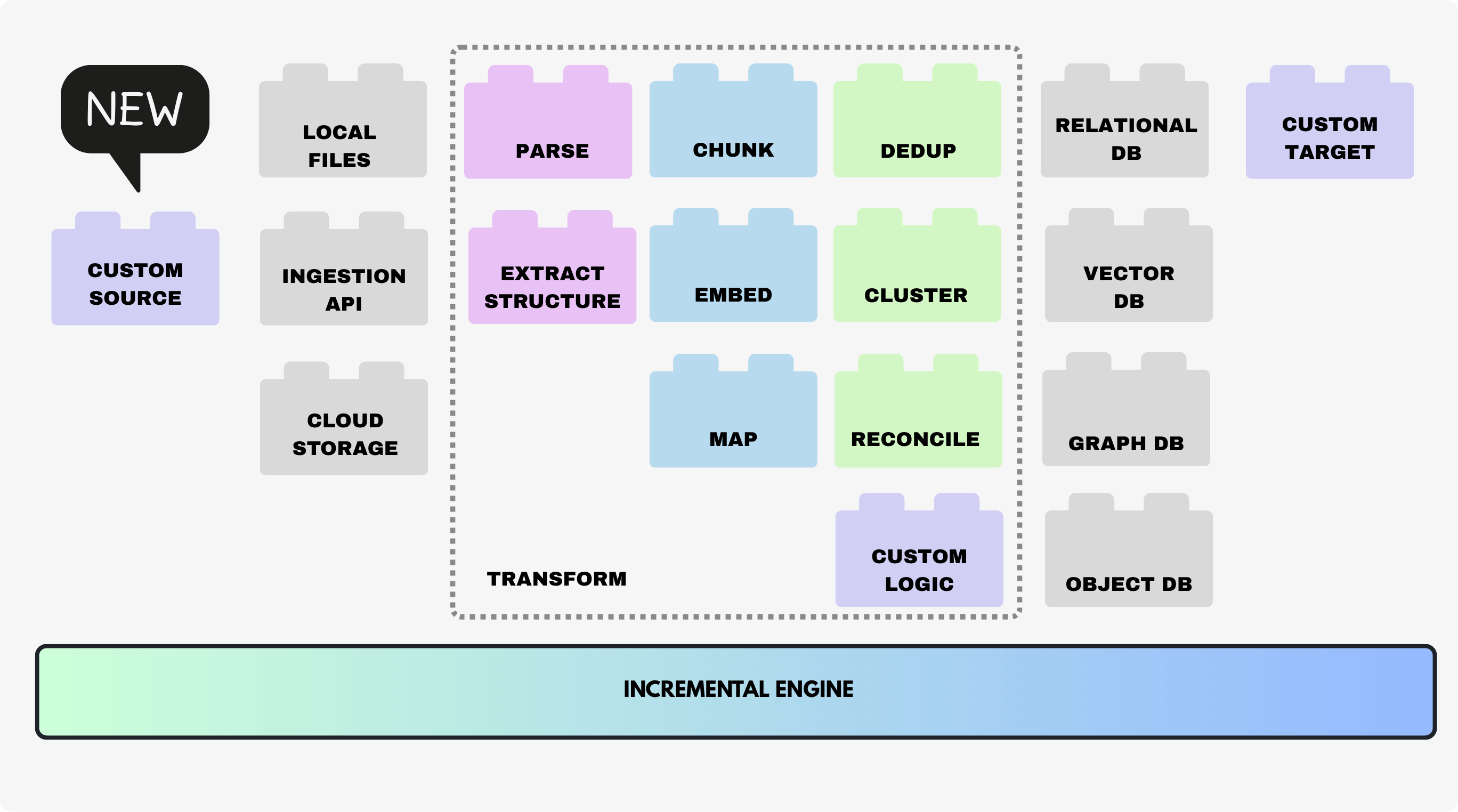
Assemble data pipelines with flexibility
CocoIndex flows were designed to be modular, composable, and declarative. With custom sources, you can now bring your own “building blocks” into the system, allowing you to read from internal tools, legacy systems, or any external service — even if there’s no pre-built connector.
In addition, CocoIndex also offers:
- Custom Targets – send data wherever you need, from local files to databases to proprietary systems, with full support for incremental updates and flow tracking.
- Custom Transformations – implement domain-specific transformations within your flows.
- Tons of Native Building Blocks – hundreds of sources, targets, and transformations are already included, letting you swap components in a single line of code.
All with standard interface lets you rapidly assemble AI-ready data pipelines. You can mix and match sources, transformations, and targets to build end-to-end workflows that are incremental, traceable, and explainable.
What's a custom source?
A custom source defines how CocoIndex reads data from an external system.
Custom sources are defined by two components:
- A source spec that configures the behavior and connection parameters for the source.
- A source connector that handles the actual data reading operations. It provides the following required methods:
create(): Create a connector instance from the source spec.list(): List all available data items. Return keys.get_value(): Get the full content for a specific data item by given key.
1. Source Spec
The source spec defines configuration parameters for your custom source. It's similar to a dataclass.
class CustomSource(cocoindex.op.SourceSpec):
"""
Custom source for my external system.
"""
param1: str
param2: int | None = None
2. Source Connector
The source connector implements the logic for reading data. For now we don’t expose the API to get change stream from source yet - for simplicity. As long as the source provides an ordinal in list(), it’s usually efficient enough for us to detect changes by refresh-interval-based live update. We’ll add change stream support soon, and reach out to us if you need this!
Data access methods
It handles the actual reading operations - discovering available data and retrieving specific content.
Here’s a typical skeleton of a custom source connector:
@cocoindex.op.source_connector(
spec_cls=CustomSource,
key_type=DataKeyType,
value_type=DataValueType
)
class CustomSourceConnector:
@staticmethod
async def create(spec: CustomSource) -> "CustomSourceConnector":
"""Initialize connection, authenticate, and return connector instance."""
...
async def list(self, options: SourceReadOptions) -> AsyncIterator[PartialSourceRow[DataKeyType, DataValueType]]:
"""List available data items with optional metadata (ordinal, content)."""
...
async def get_value(self, key: DataKeyType, options: SourceReadOptions) -> PartialSourceRowData[DataValueType]:
"""Retrieve full content for a specific data item."""
...
def provides_ordinal(self) -> bool:
"""Optional: Return True if the source provides timestamps or version numbers."""
return False
1. create(spec) – Initialize your connector
- Sets up the connection to your data source using the configuration in your
SourceSpec. - Common uses: authenticate with an API, connect to a database, or validate settings.
- Can be implemented synchronously or asynchronously depending on your system.
2. list(options?) – Discover all available items
- Returns all data items from the source along with optional metadata.
- CocoIndex can request only the fields it needs — timestamps, content, or fingerprints — so your connector fetches just enough to be efficient.
- Helps CocoIndex track which items have changed without fetching everything repeatedly.
3. get_value(key, options?) – Fetch full content
- Retrieves the complete data for a given item.
- Returns content along with optional metadata like timestamps or content fingerprints.
- Works with incremental updates, so only changed items are processed.
4. provides_ordinal() – Optional hint for efficient updates
- Returns true if your source provides timestamps or version numbers.
- Allows CocoIndex to skip unchanged items and process only updates, saving time and compute.
These methods together make it easy to integrate any data source — APIs, databases, file systems, or internal tools — into CocoIndex flows while supporting incremental, AI-ready pipelines.
Data types: understanding how CocoIndex reads data
When you create a custom source in CocoIndex, your data is structured so the system can track changes efficiently and process updates incrementally.
- SourceReadOptions – CocoIndex tells the connector what to fetch. This could include timestamps or version numbers for change tracking, content fingerprints to detect updates, and full data content when needed.
- PartialSourceRow – represents a single item from your source, combining a key (what uniquely identifies the item) and data (its content and optional metadata).
- PartialSourceRowData – holds the actual content along with metadata like timestamps, version numbers, or content fingerprints. This allows CocoIndex to process only what has changed, saving time and compute.
- Key & Value Types – define what identifies an item (keys) and what information it contains (values). Keys can be simple IDs or more complex multi-field structures. Values hold the actual content fields, such as title, text, author, or creation date.
With this approach, CocoIndex can discover data, track changes, and fetch updates efficiently, making your custom sources fully compatible with incremental, AI-ready pipelines.
For full documentation on the data methods and dataTypes please see here.
Design choice: simplicity, modularity, and incrementally
CocoIndex’s source design follows a clear separation of intent and execution:
- Declarative configuration (
SourceSpec) defines what the source is. - Operational logic (
SourceConnector) defines how to read it.
This split makes each source:
- Composable — easily reused across flows and teams.
- Incremental-first — optimized to reprocess only what changes.
- Extensible — new systems can plug in without touching the core engine.
By standardizing around this pattern, CocoIndex achieves a balance between developer flexibility and system reliability — empowering teams to integrate any system seamlessly into their AI-native data workflows.
Why custom sources?
- Connect internal systems: Read from proprietary APIs or legacy databases.
- Stream incremental updates: Efficiently track changes and update flows.
- Full flexibility: Combine with custom targets to handle any workflow end-to-end.
With Custom Sources, CocoIndex empowers you to ingest any data, track changes efficiently, and plug it directly into your pipelines — no matter how unique your systems are.
Support us
⭐ Star CocoIndex on GitHub and share with your community if you find it useful!
