Quickstart
In this tutorial, we’ll build an index with text embeddings, keeping it minimal and focused on the core indexing flow.
Flow Overview
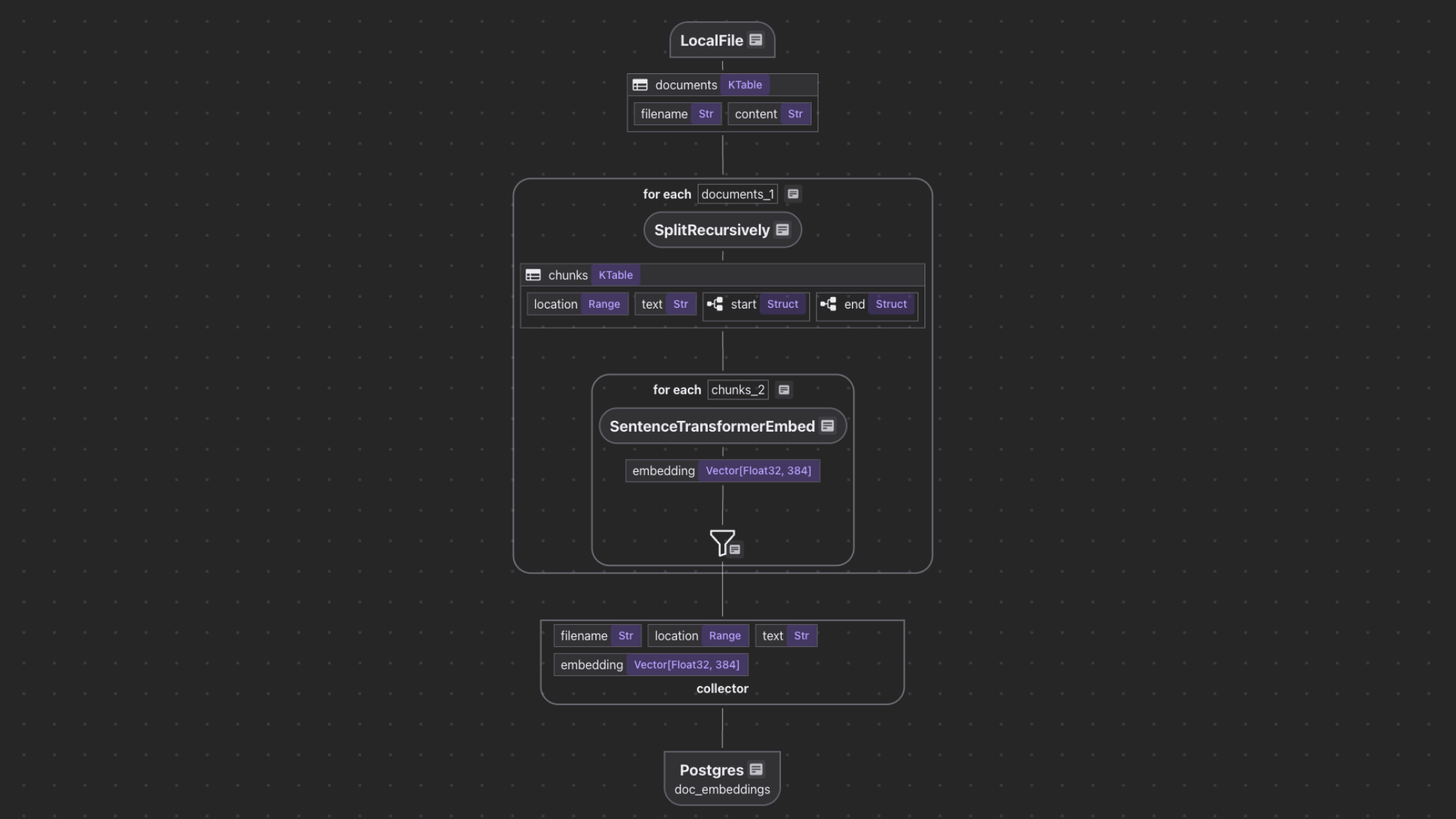
- Read text files from the local filesystem
- Chunk each document
- For each chunk, embed it with a text embedding model
- Store the embeddings in a vector database for retrieval
Setup
-
Install CocoIndex:
pip install -U 'cocoindex[embeddings]' -
Create a new directory for your project:
mkdir cocoindex-quickstart
cd cocoindex-quickstart -
Place input files in a directory
markdown_files. You may download from markdown_files.zip.
Define a flow
Create a new file main.py and define a flow.
import cocoindex
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="TextEmbedding")
def text_embedding_flow(flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope):
# ... See subsections below for function body
Add Source and Collector
# add source
data_scope["documents"] = flow_builder.add_source(
cocoindex.sources.LocalFile(path="markdown_files"))
# add data collector
doc_embeddings = data_scope.add_collector()
flow_builder.add_source will create a table with sub fields (filename, content)
Process each document
With CocoIndex, it is easy to process nested data structures.
with data_scope["documents"].row() as doc:
# ... See subsections below for function body
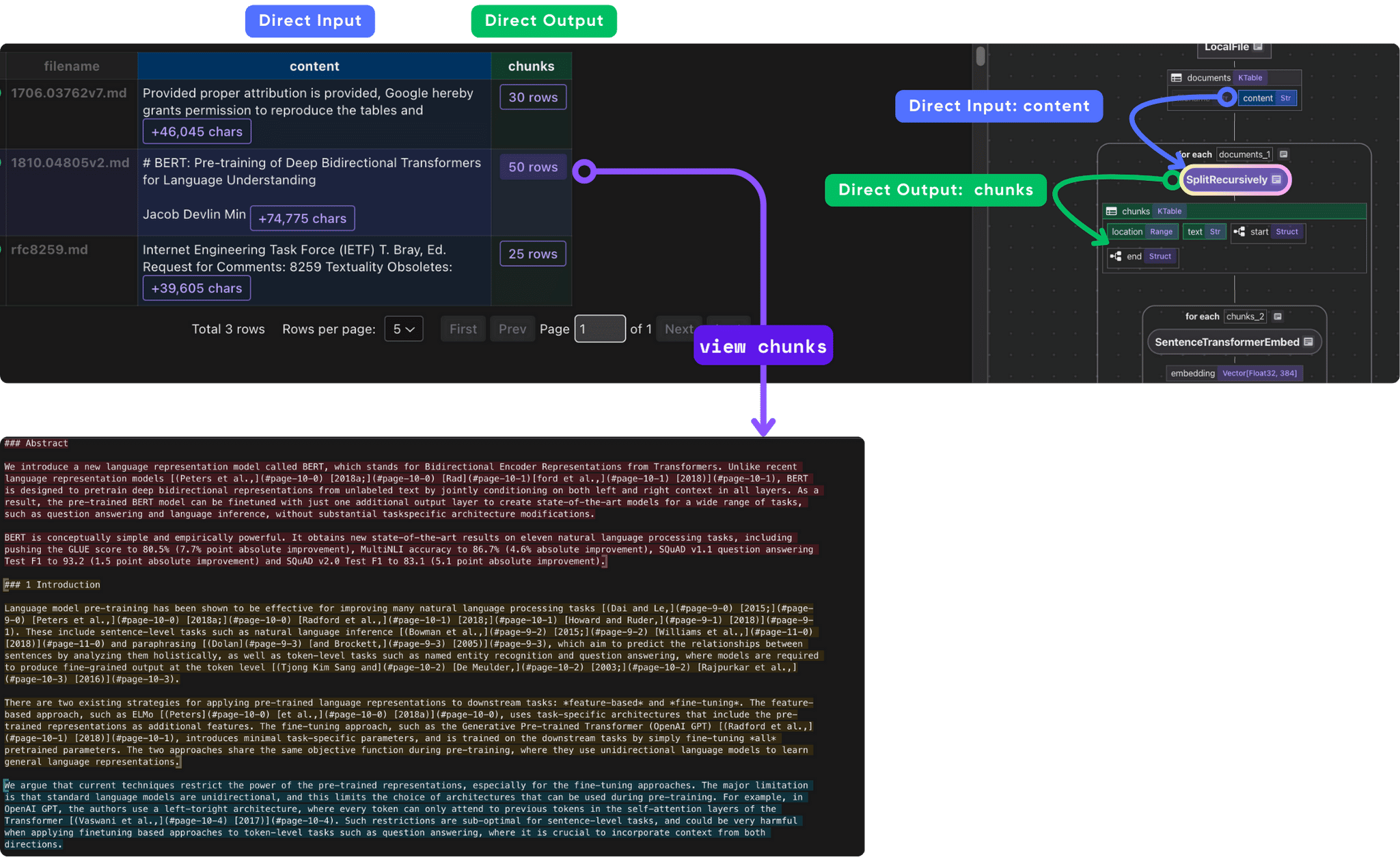
Chunk each document
doc["chunks"] = doc["content"].transform(
cocoindex.functions.SplitRecursively(),
language="markdown", chunk_size=2000, chunk_overlap=500)
We extend a new field chunks to each row by transforming the content field using SplitRecursively. The output of the SplitRecursively is a KTable representing each chunk of the document.
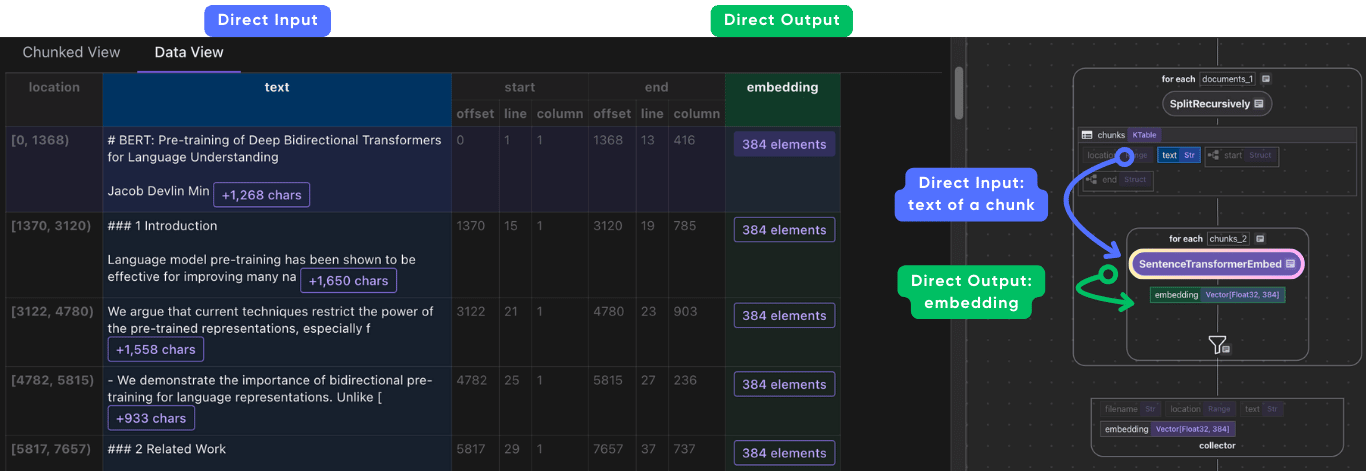
Embed each chunk and collect the embeddings
with doc["chunks"].row() as chunk:
# embed
chunk["embedding"] = chunk["text"].transform(
cocoindex.functions.SentenceTransformerEmbed(
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
)
# collect
doc_embeddings.collect(
filename=doc["filename"],
location=chunk["location"],
text=chunk["text"],
embedding=chunk["embedding"],
)
This code embeds each chunk using the SentenceTransformer library and collects the results.
Export the embeddings to Postgres
doc_embeddings.export(
"doc_embeddings",
cocoindex.storages.Postgres(),
primary_key_fields=["filename", "location"],
vector_indexes=[
cocoindex.VectorIndexDef(
field_name="embedding",
metric=cocoindex.VectorSimilarityMetric.COSINE_SIMILARITY,
)
],
)
CocoIndex supports other vector databases as well, with 1-line switch.
TargetsRun the indexing pipeline
-
Specify the database URL by environment variable:
export COCOINDEX_DATABASE_URL="postgresql://cocoindex:cocoindex@localhost:5432/cocoindex"
Make sure your Postgres server is running before proceeding. See how to launch CocoIndex for details.
-
Build the index:
cocoindex update main
CocoIndex will run for a few seconds and populate the target table with data as declared by the flow. It will output the following statistics:
documents: 3 added, 0 removed, 0 updated
That's it for the main indexing flow.
End to end: Query the index (Optional)
If you want to build a end to end query flow that also searches the index, you can follow the simple_vector_index example.
Next Steps
Next, you may want to:
- Learn about CocoIndex Basics.
- Explore more of what you can build with CocoIndex in the examples directory.