Real-time data transformation from Google Drive
This guide shows how to build a real-time data pipeline with CocoIndex to transform and index files from Google Drive. It walks through setting up Google credentials, configuring CocoIndex, and builds a vector index for semantic search.
Prerequisites
Install Postgres
If you don't have Postgres installed, please refer to the installation guide.
Enable Google Drive access by service account
CocoIndex provides a native built-in integration to support Google Drive as a source.
GoogleDrive Source1. Register / login in Google Cloud.
First, you need to create a Google Cloud account if you don't have one already. Go to the Google Cloud Console and sign up or sign in.
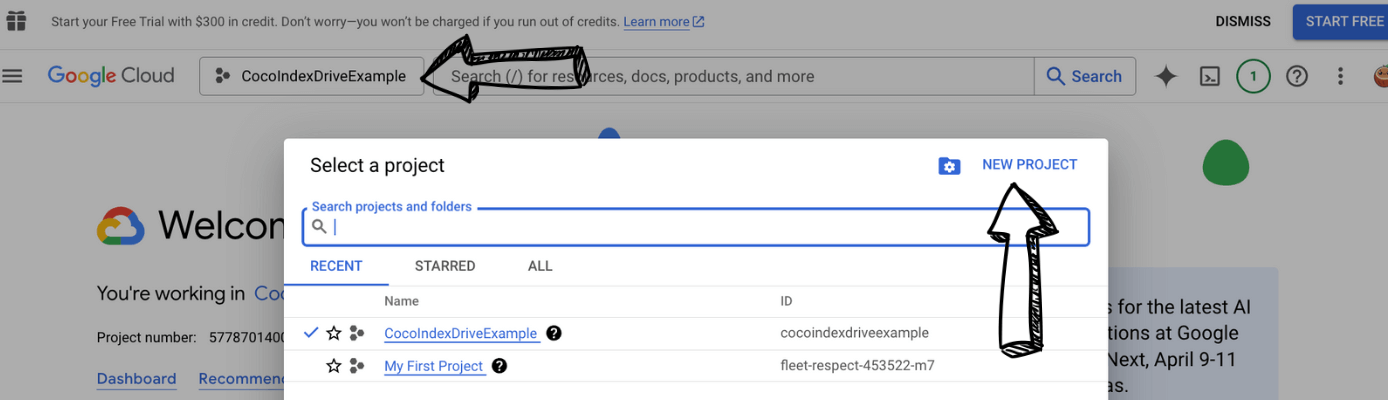
2. Select or create a GCP project
Once you've logged into Google Cloud Console, you need to select an existing project or create a new one. Click on the project selector dropdown at the top of the page:
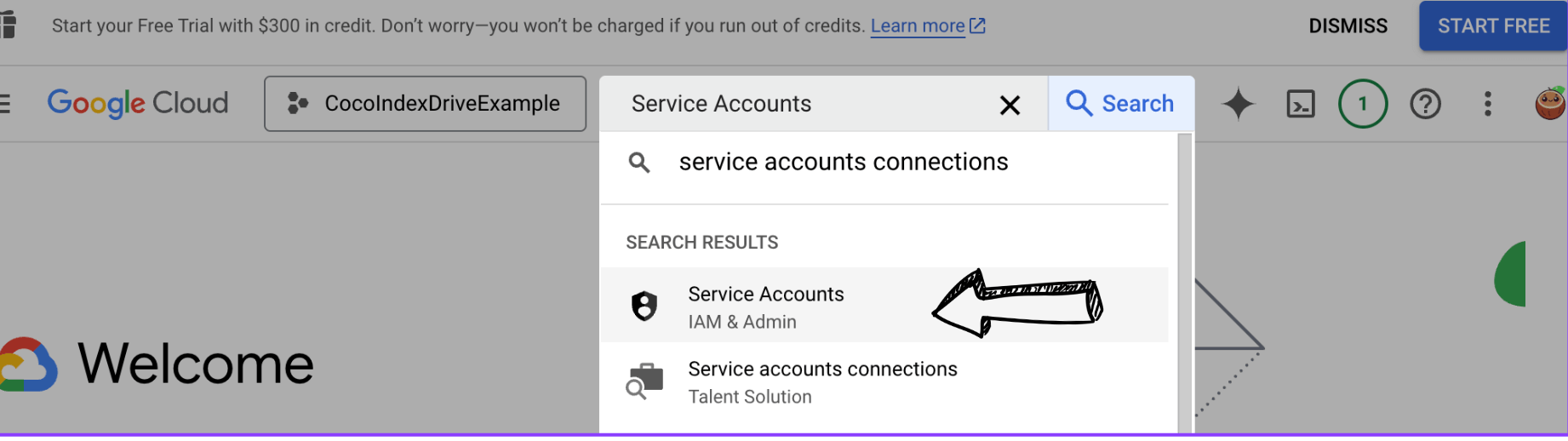
3. Create a Service Account
-
In Google Cloud Console, search for Service Accounts, to enter the IAM & Admin / Service Accounts page.
-
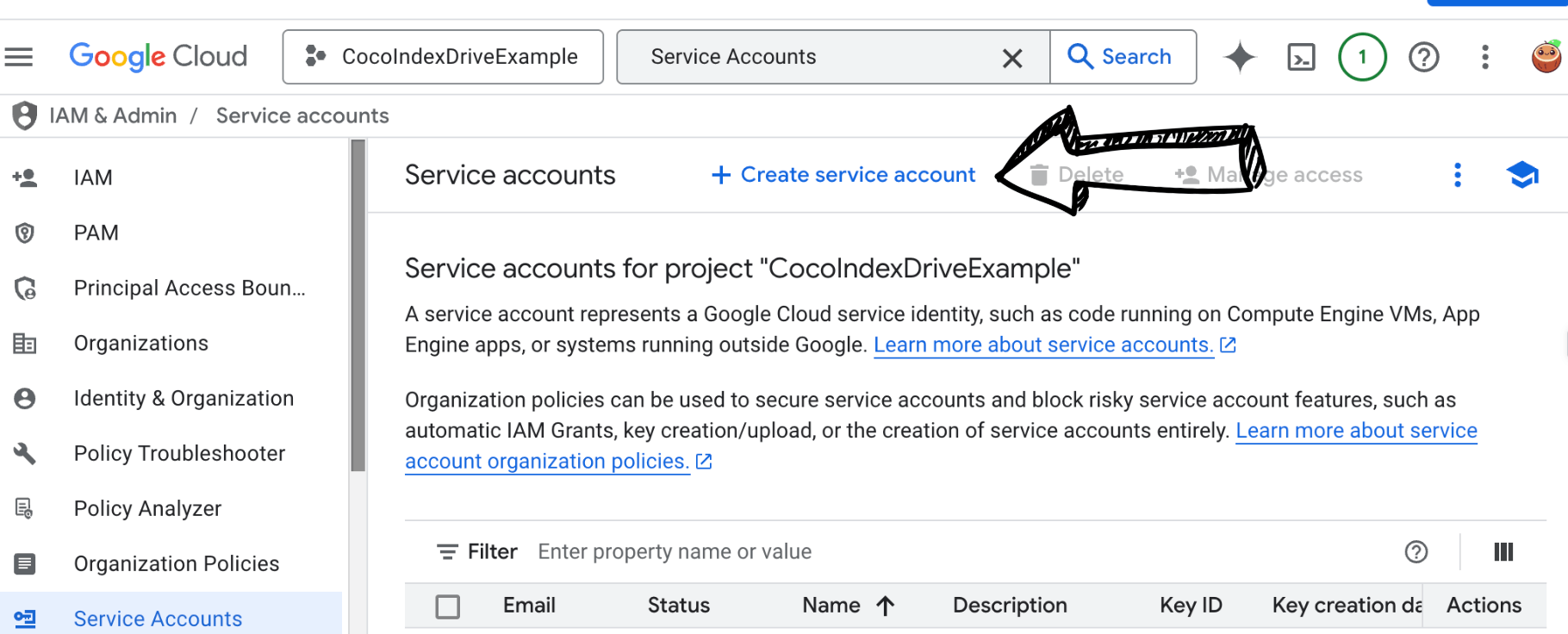
Click on "CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT" at the top of the page:
-
Fill in the service account name, e.g.
cocoindex-test.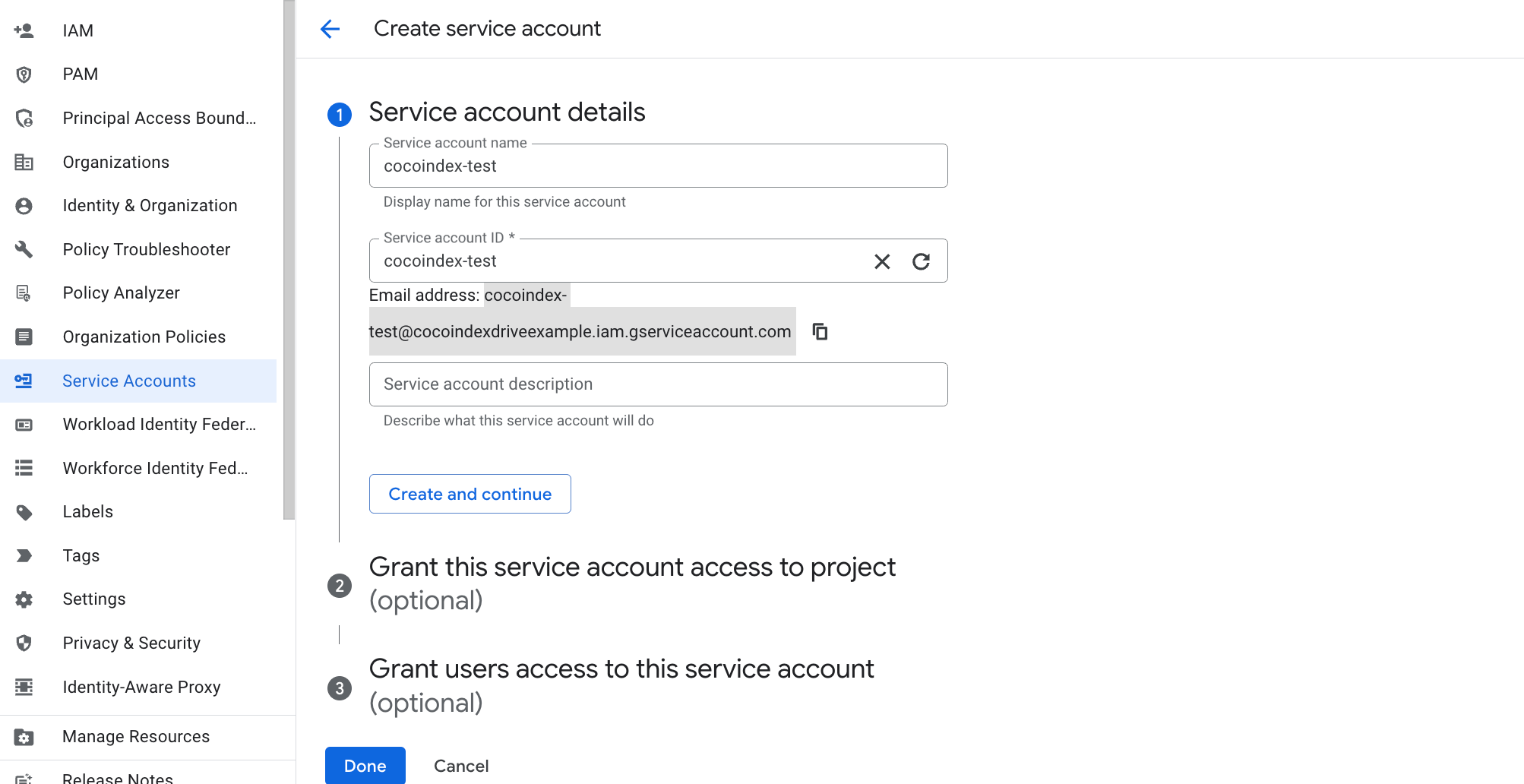
And make a note on that email address, you will need it in the later step.
-
Click on "CREATE" to create the service account. You will see the service account created successfully.
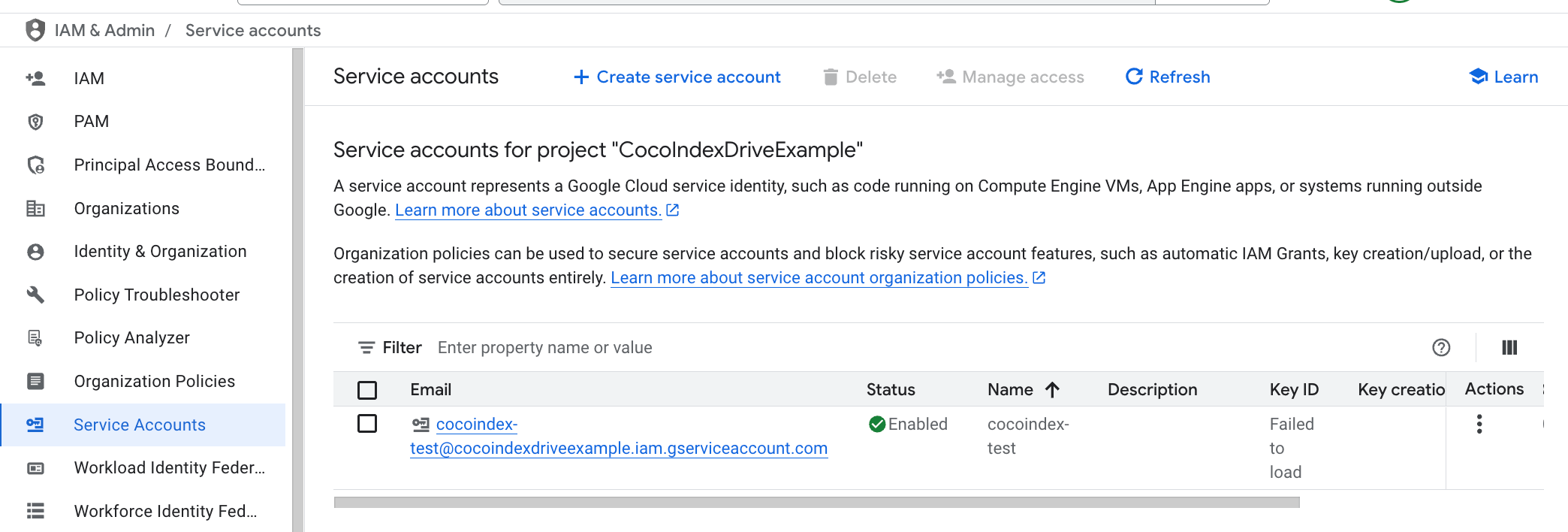
4. Create and download the key for the service account
-
Click on "Actions" and select "Manage Keys".
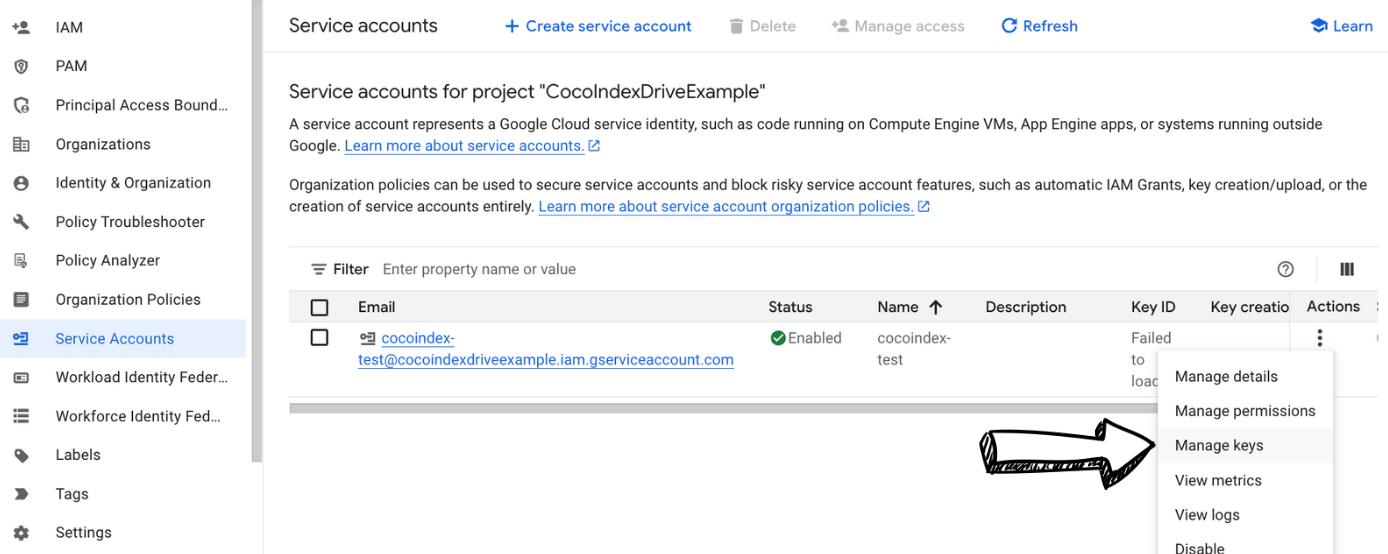
-
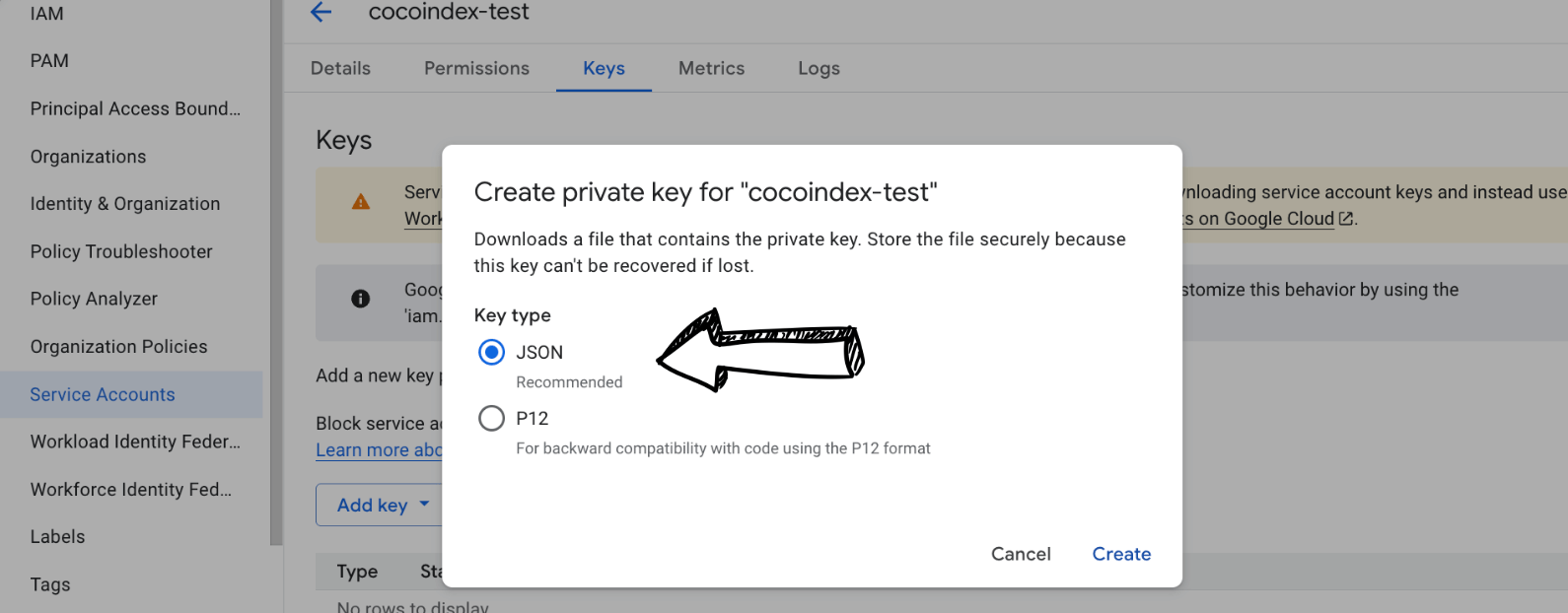
Select "Add Key" and select "Create new key".
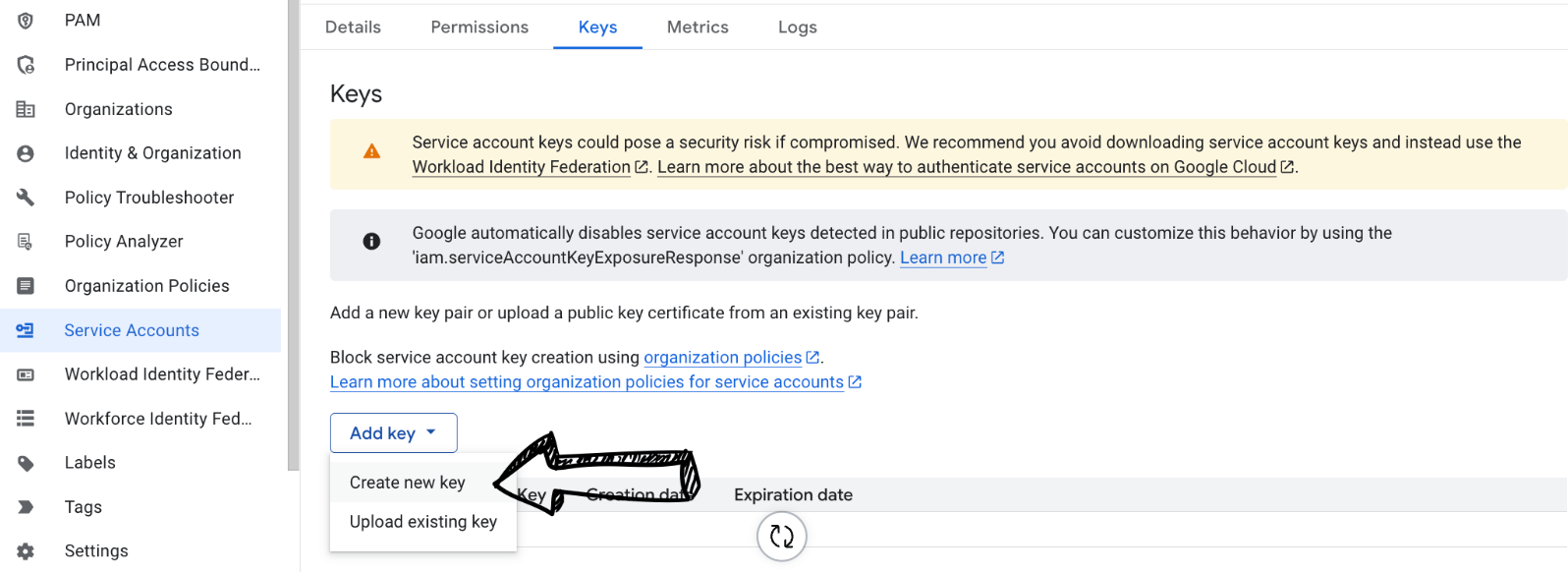
Choose "JSON" as the key type and click "Create".
-
The key file will be downloaded to your computer. Depending on the browser settings, it starts downloading automatically or may pop up a dialog for the download location. Keep this file secure as it provides access to your Google Drive resources. It looks like this:
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "cocoindexdriveexample",
"private_key_id": "key_id",
"private_key": "PRIVATE_KEY",
"client_email": "[email protected]",
"client_id": "id",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/cocoindex-test%40cocoindexdriveexample.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"universe_domain": "googleapis.com"
}
5. Enable Google Drive API
Search for "Google Drive API" in Google Cloud Console and enable it.
6. Prepare and share a folder
-
Create a new folder or use an existing folder in your Google Drive.
- For this project, we will create a folder in my own Google Drive, and share it with the service account email address we created in Step 3. For example,
[email protected]. - My example Google Drive folder is here.
- The files are also available in the example repo.
- For this project, we will create a folder in my own Google Drive, and share it with the service account email address we created in Step 3. For example,
-
Share the folder with the service account. Enter the service account email address (e.g.,
[email protected]) and give it "Viewer" access.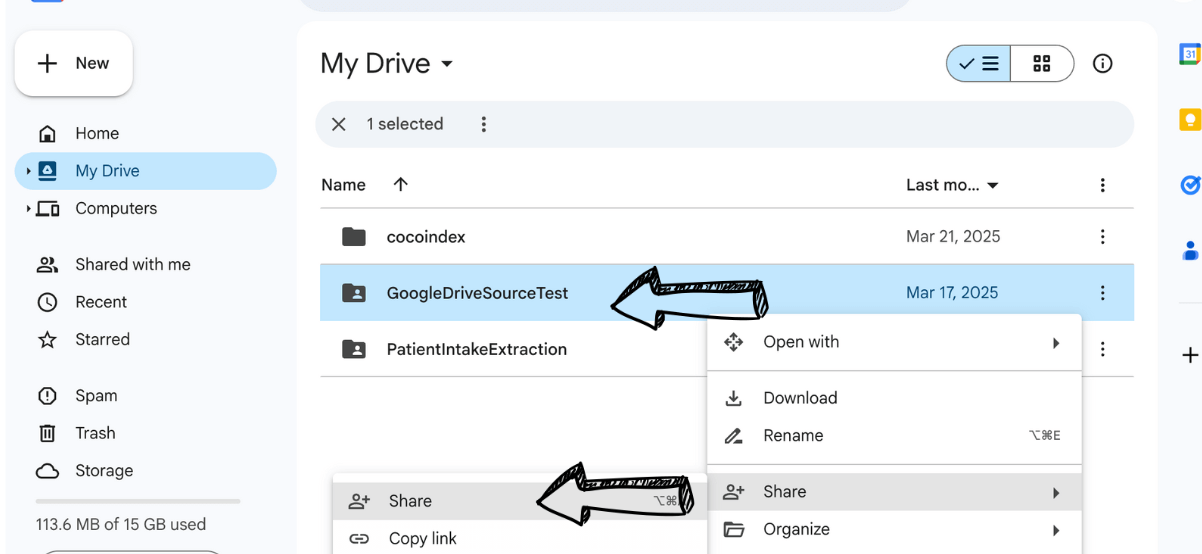
-
Note the folder ID from the URL when you open the folder. The URL will look like:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1AbCdEfGhIjKlMnOpQrStUvWxYzThe folder ID is the part after
folders/(in this example:1AbCdEfGhIjKlMnOpQrStUvWxYz). You'll need this folder ID when connecting to the Google Drive API.
Project setup
-
Create a
pyproject.tomlfile in the root directory.[project]
name = "gdrive-text-embedding"
version = "0.1.0"
description = "Simple example for cocoindex: build embedding index based on Google Drive files."
requires-python = ">=3.11"
dependencies = ["cocoindex>=0.2.4", "python-dotenv>=1.0.1"] -
Set up
.envCreate a.envfile in the root directory and add the following: You can copy it from the.env.examplefile.# Postgres database address for cocoindex
COCOINDEX_DATABASE_URL=postgres://cocoindex:cocoindex@localhost/cocoindex
# Google Drive service account credential path.
#! PLEASE FILL IN
GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_CREDENTIAL=/path/to/service_account_credential.json
# Google Drive root folder IDs, comma separated.
#! PLEASE FILL IN YOUR GOOGLE DRIVE FOLDER ID
GOOGLE_DRIVE_ROOT_FOLDER_IDS=1AbCdEfGhIjKlMnOpQrStUvWxYz
Define CocoIndex Flow
Let's define the CocoIndex flow to build text embeddings from Google Drive.
First, let's load the files from Google Drive as a source. CocoIndex provides a GoogleDrive source as a native built-in source. You just need to provide the service account credential path and the root folder IDs.
1. Load the files from Google Drive
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="GoogleDriveTextEmbedding")
def gdrive_text_embedding_flow(flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope):
"""
Define an example flow that embeds text into a vector database.
"""
credential_path = os.environ["GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_CREDENTIAL"]
root_folder_ids = os.environ["GOOGLE_DRIVE_ROOT_FOLDER_IDS"].split(",")
data_scope["documents"] = flow_builder.add_source(
cocoindex.sources.GoogleDrive(
service_account_credential_path=credential_path,
root_folder_ids=root_folder_ids))
doc_embeddings = data_scope.add_collector()
flow_builder.add_source will create a table with the following sub fields, see documentation here.
filename(key, type:str): the filename of the file, e.g.dir1/file1.mdcontent(type:strifbinaryisFalse, otherwisebytes): the content of the file
Rest of the flow
For the rest of the flow, we can follow the tutorial Simple Vector Index. The entire project is available here.
Query and test your index
🎉 Now you are all set!
Run the following command to setup and update the index.
cocoindex update --setup main
You'll see the index updates state in the terminal. For example, you'll see the following output:
documents: 3 added, 0 removed, 0 updated
CocoInsight
CocoInsight is a comprehensive web interface to understand your data pipeline and interact with the index. CocoInsight has zero data retention with your pipeline data.
cocoindex server -ci main