Real-time data transformation pipeline with Amazon S3 bucket, SQS and CocoIndex
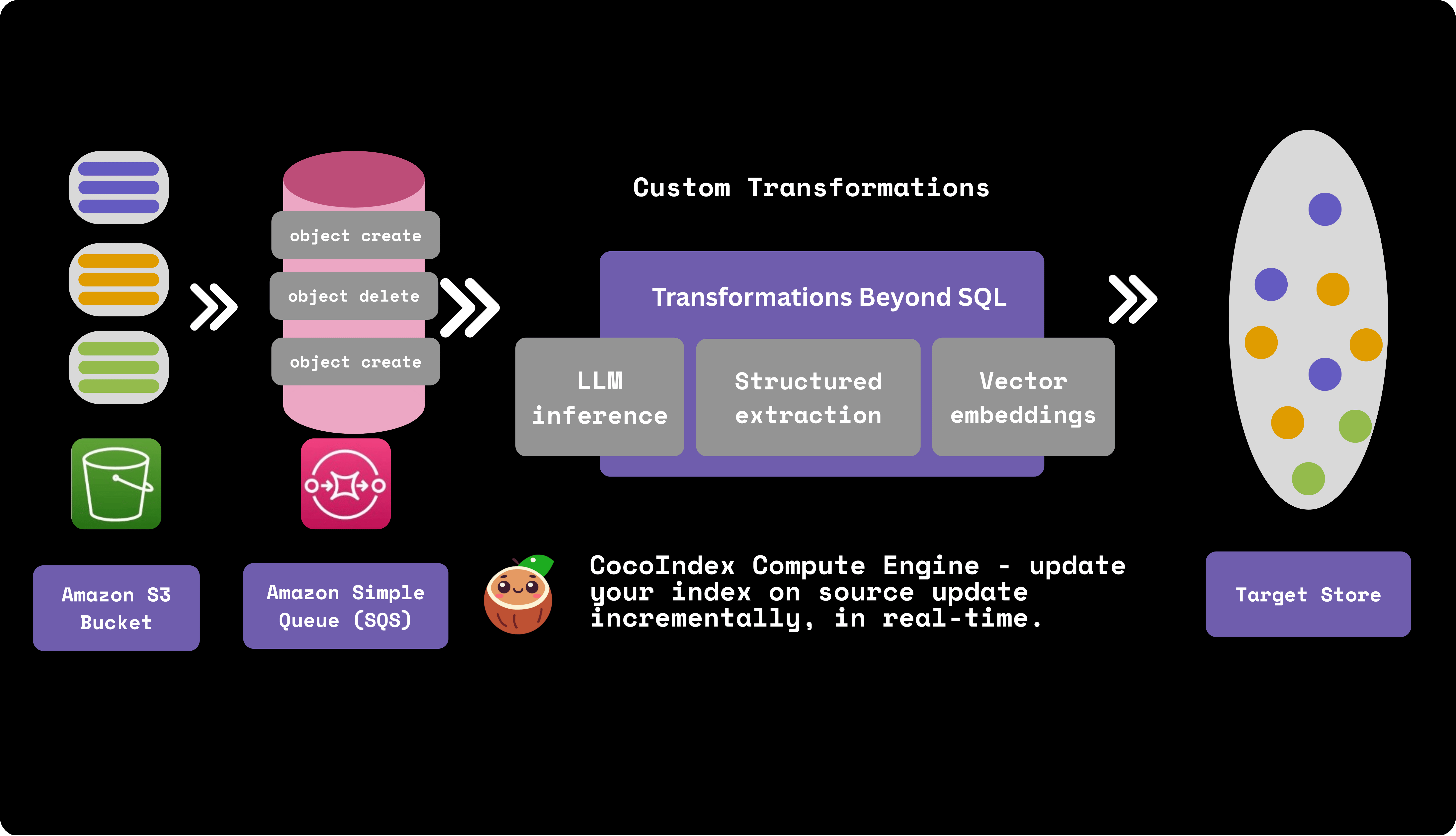
CocoIndex natively supports Amazon S3 as a source and integrates with AWS SQS for real-time, incremental S3 data processing.
AWS SQS
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a message queuing service that provides a reliable, highly-scalable hosted queue for storing messages as they travel between applications or microservices. When S3 files change, SQS queues event messages containing details like the event type, bucket, object key, and timestamp. Messages stay in the queue until processed, so no events are lost.
Live update out of the box with SQS
CocoIndex provides two modes to run your pipeline, one time update and live update, both leverage the incremental processing. Particularly with AWS SQS, you could leverage the live update mode - where CocoIndex continuously monitors and reacts to the events in SQS, updating the target data in real-time. This is ideal for use cases where data freshness is critical.
Live Update TutorialHow does it work?
Let's take a look at simple example of how to build a real-time data transformation pipeline with S3 and CocoIndex. It builds a vector database of text embeddings from markdown files in S3.
S3 bucket and SQS setup
Please follow the documentation to setup S3 bucket and SQS queue.
Amazon S3 SourceS3 bucket
- Creating an AWS account.
- Configuring IAM permissions.
- Configure policies. You'll need at least the
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccesspolicy, and if you want to enable change notifications, you'll also need theAmazonSQSFullAccesspolicy.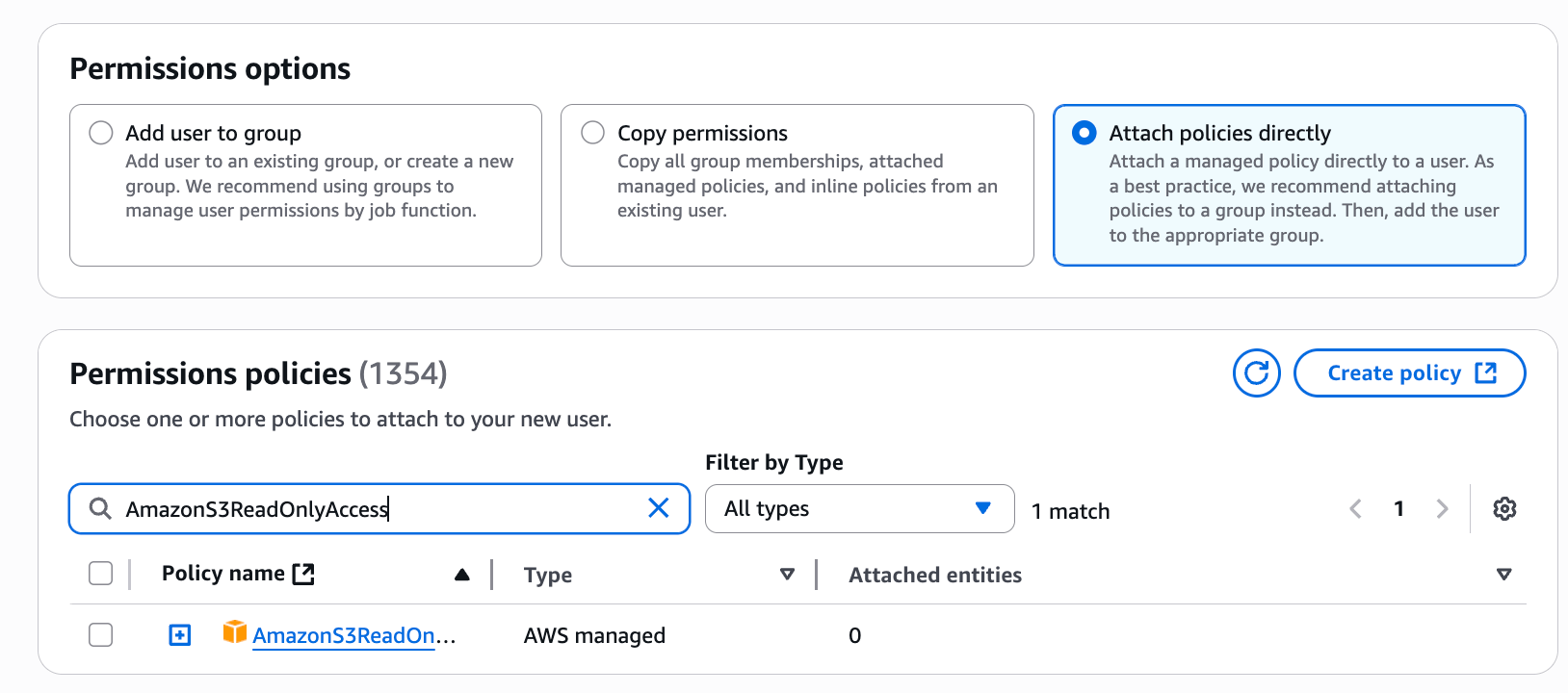
SQS queue
For real-time change detection, you'll need to create an SQS queue and configure it to receive notifications from your S3 bucket.
Please follow the documentation to configure the S3 bucket to send event notifications to the SQS queue.
Particularly, the SQS queue needs a specific access policy that allows S3 to send messages to it.
{
...
"Statement": [
...
{
"Sid": "__publish_statement",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "s3.amazonaws.com"
},
"Resource": "${SQS_QUEUE_ARN}",
"Action": "SQS:SendMessage",
"Condition": {
"ArnLike": {
"aws:SourceArn": "${S3_BUCKET_ARN}"
}
}
}
]
}
Then you can upload your files to the S3 bucket.
Define Indexing Flow
Flow Design
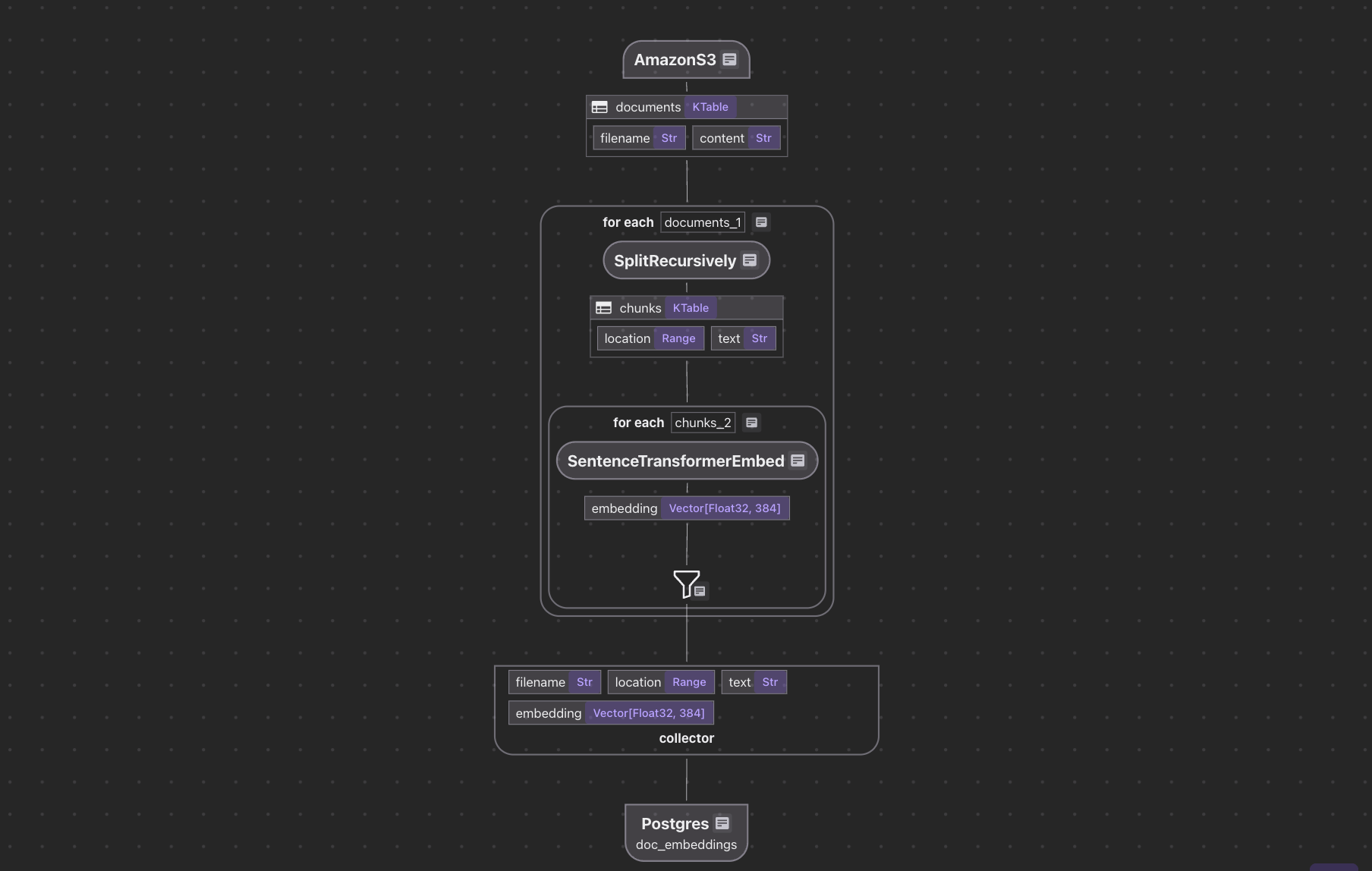
The flow diagram illustrates how we'll process our codebase:
- Read text files from the Amazon S3 bucket
- Chunk each document
- For each chunk, embed it with a text embedding model
- Store the embeddings in a vector database for retrieval
AWS File Ingestion
Define the AWS endpoint and the SQS queue name in .env file:
# Database Configuration
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://localhost:5432/cocoindex
# Amazon S3 Configuration
AMAZON_S3_BUCKET_NAME=your-bucket-name
AMAZON_S3-SQS_QUEUE_URL=https://sqs.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/123456789/S3ChangeNotifications
Define indexing flow and ingest from Amazon S3 SQS queue:
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="AmazonS3TextEmbedding")
def amazon_s3_text_embedding_flow(
flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope
):
bucket_name = os.environ["AMAZON_S3_BUCKET_NAME"]
prefix = os.environ.get("AMAZON_S3_PREFIX", None)
sqs_queue_url = os.environ.get("AMAZON_S3_SQS_QUEUE_URL", None)
data_scope["documents"] = flow_builder.add_source(
cocoindex.sources.AmazonS3(
bucket_name=bucket_name,
prefix=prefix,
included_patterns=["*.md", "*.mdx", "*.txt", "*.docx"],
binary=False,
sqs_queue_url=sqs_queue_url,
)
)
This defines a flow that reads text files from the Amazon S3 bucket.
Rest of the flow
For the rest of the flow, we can follow the tutorial Simple Vector Index. The entire project is available here.
Run the flow with live update
cocoindex update main.py -L
-L option means live update, see the documentation for more details.
And you will have a continuous long running process that will update the vector database with any updates in the S3 bucket.